
Back Nama Afrikaans لغة ناما Arabic Idioma khoekhoe AST Койкойски език Bulgarian Nama Catalan Namaština Czech Khoekhoegowab German Nama lingvo Esperanto Idioma khoekhoe Spanish Nama keel Estonian
| Khoekhoe | |
|---|---|
| Nama/Damara | |
| Khoekhoegowab | |
| Native to | Namibia, Botswana and South Africa |
| Region | Orange River, Great Namaland, Damaraland |
| Ethnicity | Khoikhoi, Nama, Damara, Haiǁom, ǂKhomani |
Native speakers | 200,000 ± 10,000 (2011)[1] |
Khoe–Kwadi
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:naq – Khoekhoe, Namahgm – Haiǁom |
| Glottolog | nort3245 Subfamily: North Khoekhoenama1264 Language: Namahaio1238 Language: Haiǁom-Akhoe |
| ELP | Khoekhoe |
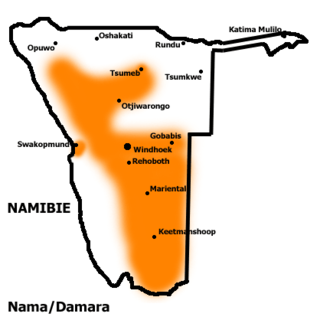 The distribution of the Nama language in Namibia | |
| The Khoe language | |
|---|---|
| Person | Khoe-i |
| People | Khoekhoen |
| Language | Khoekhoegowab |
The Khoekhoe /ˈkɔɪkɔɪ/ KOY-koy language (Khoekhoegowab), also known by the ethnic terms Nama (Namagowab) /ˈnɑːmə/ NAH-mə,[3] Damara (ǂNūkhoegowab), or Nama/Damara[4][5] and formerly as Hottentot,[b] is the most widespread of the non-Bantu languages of Southern Africa that make heavy use of click consonants and therefore were formerly classified as Khoisan, a grouping now recognized as obsolete. It belongs to the Khoe language family, and is spoken in Namibia, Botswana, and South Africa primarily by three ethnic groups: Namakhoen, ǂNūkhoen, and Haiǁomkhoen.
- ^ Brenzinger, Matthias (2011) "The twelve modern Khoisan languages." In Witzlack-Makarevich & Ernszt (eds.), Khoisan languages and linguistics: proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium, Riezlern / Kleinwalsertal (Research in Khoisan Studies 29). Cologne: Rüdiger Köppe Verlag.
- ^ "Constitution of the Republic of South Africa, 1996 – Chapter 1: Founding Provisions". gov.za. Retrieved 6 December 2014.
- ^ Laurie Bauer, 2007, The Linguistics Student's Handbook, Edinburgh
- ^ Haacke, Wilfrid H. G. (2018), Kamusella, Tomasz; Ndhlovu, Finex (eds.), "Khoekhoegowab (Nama/Damara)", The Social and Political History of Southern Africa's Languages, Palgrave Macmillan UK, pp. 133–158, doi:10.1057/978-1-137-01593-8_9, ISBN 978-1-137-01592-1
- ^ a b "Khoekhoe languages". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ "Hottentot". Oxford Reference. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search